A home aquarium with fish is an excellent option for those who want to have an animal but do not have the opportunity to train, raise, or play with it. In addition, modern aquarium solutions allow the fish house to fit into any house style harmoniously, making it a decorative element.
Beginning aquarists are often interested in the choice of fish, their character traits, and the conditions for keeping and caring for them. This article will teach you everything about the features of this species, such as betta fish.
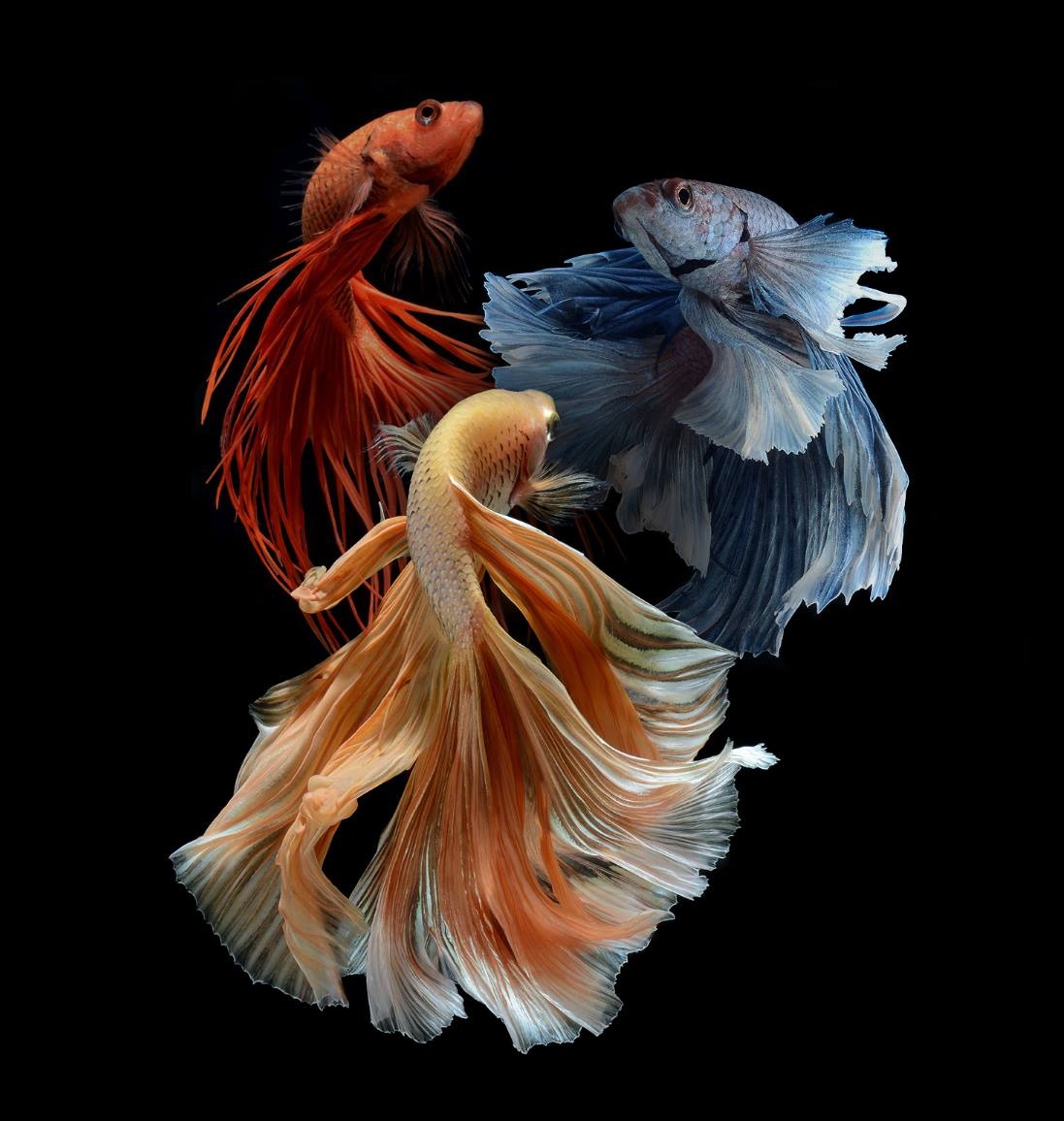

External Description Of Betta Fish
This species probably attracted your attention in pet stores because its main difference is its bright color, which can include all the colors of the rainbow and its expressive veil-shaped fins.
Each color has its exciting name: Mustard Gas, Lemon Meringue, Pharoah, Super Black/Super Red, Thai Flag, and many others. Males are brighter in color than females. The fin’s size will also help distinguish a boy from a girl: in boys, it is much more luxurious and voluminous; in girls, it is more miniature.
The fish are small and, in captivity, grow no more than 7-8 cm in length.
Choosing an aquarium, its contents, and additional decor
Betta fish should not be kept in large numbers in a small aquarium – in this case, they will begin to divide the territory actively. It is also recommended to keep only one male cockerel in a small aquarium; in larger aquariums, you can try to add another one, but at first, you need to observe the manifestations of characteristic features to avoid collisions. If you want to keep several males of different species, place particular partitions in the aquarium.
The optimal temperature for keeping betta fish is 25-28 °C. The aquarium’s water must not be filled, not reaching 10-12 cm from the edge. The aquarium must have a lid so that particularly active fish do not fall out of the water when jumping.

Experts recommend decorating the aquarium with various live plants, stones, corals, castles, and shells, which help create the most natural habitat for fish. You can turn your home aquarium into a real work of art, but you need to use a little imagination.

Feeding the fish
The fish are fed 1-2 times a day. Overfeeding threatens obesity and can even lead to death. It is recommended that fish be eaten in amounts of 5% of their body weight. The daily diet of bettas may include:
- dry flakes;
- granular feed;
- live food (worms, tubifex, bloodworms, crustaceans) is also acceptable in dry or frozen form.
Do not mix different types of food in one feeding. If you switch your fish to a different kind of food, then introduce it gradually, increasing the percentage of the new product per serving.
After birth, babies need to be fed more often, but in small quantities. Dry food for adult fish is strictly forbidden when feeding. It is necessary to start feeding with plankton, gradually transferring the Artemia larvae to a standard diet.
When purchasing food, pay attention to the shelf life. At home, keep them closed and away from moisture.
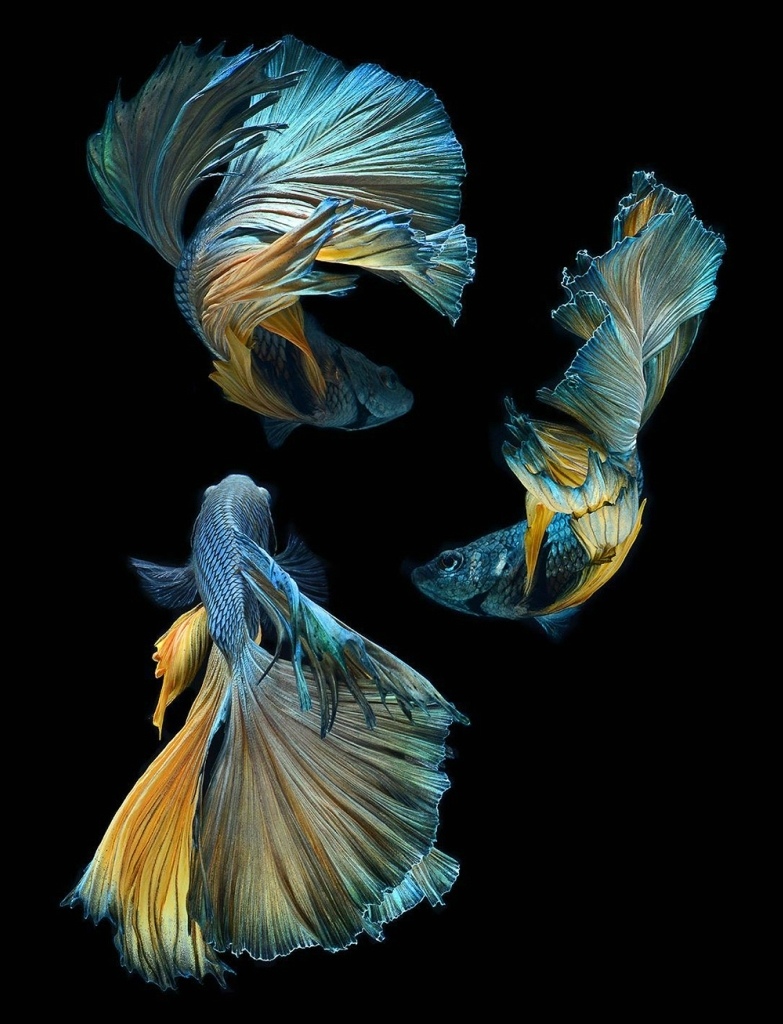

Lifespan and Compatibility
With proper care and compliance with the conditions of detention, fish in captivity live from 2 to 4.5 years.
Being the owners of gorgeous colors, betta fish have a very aggressive character.
It would be best to be especially vigilant when breeding a fighting species with peace-loving fish since the latter may have damaged whiskers, tails, and fins. Males behave the most aggressively, so at first, you should pay attention to conflicts within the aquarium and, if necessary, relocate the fish to avoid the death of one of them.
Under no circumstances should you add brightly colored fish with large fins to your bettas; such fish are automatically perceived as rivals and will immediately be tested for strength. Small fish, less than 4 cm, are automatically perceived by them as potential victims.

Interesting fact: in the homeland of this betta fish, there is a whole craze for fighting fish in Asia. Such events attract spectators, and bets are placed on the battle’s outcome.
Adding a small amount of salt to the aquarium (at the rate of 0.5 tsp per 5 liters) will help calm the fish.
If you already have an aquarium with fish and want to add a fighting species, we strongly recommend adding only a young betta fish. The fish’s age determines its conflict with other species.
The temperature regime is also worth remembering. Of course, heat-loving betta fish will not get along with the inhabitants of calm waters and, therefore, need to be kept separately.
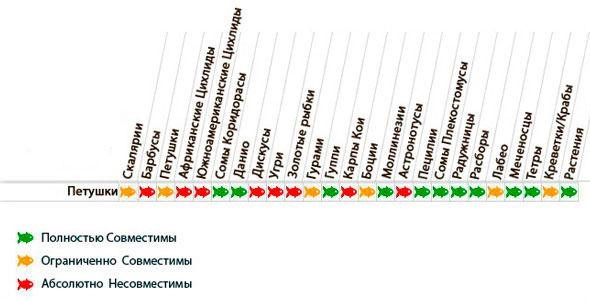
Experienced breeders have compiled a table of compatibility of betta fish with individuals of other species, which will help you choose a good match.
Fish diseases
Just like other pets, fish can get sick. What do you think you should pay attention to?
- Dull color and loss of color.
- Lethargy.
- Frequent stay at the bottom of the aquarium.
- Lack of appetite.
- Damage to scales, tears in tail and fins.
- Bloating of any part of the body.
Having noticed these and similar deviations, the fish should be relocated, and a doctor should be consulted on the issues of drawing up a treatment regimen and preventing disease in healthy fish.
In the event of a fatal outcome, the aquarium’s contents must be disinfected, the water replaced, and preventive measures must be carried out.
Let’s look at several common diseases and methods of treating them:
Ichthyophthiriasis

The following identifying signs can recognize the disease:
- the fish itches on objects;
- the body and fins are covered with white dots or spots;
- lethargy, lack of appetite.
The disease occurs due to poor care, a small space inhabited by many fish, poor nutrition, or low water temperature.
What to do? A sick fish must be transplanted from a healthy fish into the water with a temperature of about 25-30° C. Salt (sea or table) and drugs such as anti-steam, methylene blue, and penicillin-5 are added to the water. Symptoms should disappear after a couple of days. Healthy fish also require a water change and general disinfection of the aquarium.
Fin rot

The disease is easily determined by damage to the fins, gluing, clouding, and other manifestations of deviation from the norm. Occurs as a result of improper care of the aquarium or insufficient cleaning.
This infectious disease can be transmitted to other fish, so they must be separated. Treatment is carried out with antibacterial drugs such as streptocide (1.5 grams per 10 liters of water), fiosept, antipar, and table salt at 7 grams per 10 liters of water.
The water in the main aquarium is changed, and filters, soil, plants, and accessories are washed with a solution of penicillin-5.
Exophthalmos (bulging eyes)

It manifests itself in enlargement of the eye orbits and the appearance of opacities or growths. The fish behaves sluggishly, has no appetite, and swims mainly at the bottom of the aquarium. The cause may be poor-quality water, inappropriate medications, or intoxication of the fish’s body.
The fish is transplanted into a separate container and treated with Epsom salt (magnesium sulfate).
The water in the main aquarium must also be replaced, and the contents of the aquarium must be disinfected.
Aquarist’s first aid kit
We have compiled a small list of first aid and preventative medications, many of which are probably in your home medicine cabinet.
Alcohol 5% iodine solution – used to treat ichthyophthyriasis and treat wounds.
Bicillin-5 is applicable for the treatment of bacterial diseases.
Metronidazole is a drug for poisoning and parasitic diseases.
Human interferon is generally used to improve immunity in aquarium fish.
Hydrogen peroxide (3%) is used for breathing problems, fish resuscitation, lack of air due to a compressor failure, and long-term fish transportation.
Chlorhexidine solution 0.05% – used to treat hands after working with an aquarium.
Vetom 1.1 is a drug for the prevention of diseases in aquarium fish. It is sold in veterinary clinics and specialized pharmacies.